
This morning at 10am PT, I’ll be joining KQED’s Forum to discuss how California can make our roads and pathways safer for bicyclists. Biking is a more climate-friendly and healthy way to get around, but sharing space on California’s roadways with vehicles is notoriously dangerous and sometimes deadly. What can be done to make biking safer and encourage more people to ride?
Joining me on the panel will be:
- Jared Sanchez, policy director, California Bicycle Coalition
- Darwin Moosavi, deputy secretary for environmental policy and housing coordination, California State Transportation Agency
- Anthony Molina, chair, Fresno County Bike Coalition
Stream live at 10am PT or tune in at 88.5 FM KQED in the San Francisco Bay Area!
Then at 6pm PT, I’ll be hosting State of the Bay on KALW, where we’ll start by interviewing State Senator Scott Wiener about his bill SB 58 to decriminalize psychedelics in California.
Then I’ll interview former Oakland Athletics vice president Andy Dolich, author of Goodbye, Oakland, about the future of the team and sports in Oakland, given the team owners’ apparent decision to relocate to Las Vegas. Can Oakland find a way to keep their last major sports franchise from leaving?
Finally, we’ll hear all about the San Francisco Mime Troupe’s new satire, Breakdown.
Tune in at 91.7 FM in the San Francisco Bay Area or stream live at 6pm PT. What comments or questions do you have for our guests? Call 866-798-TALK to join the conversation!
The California State Senate this morning (for a second time after an initial vote last night) narrowly and finally killed SB 50, a major climate-land use bill that would have allowed apartment buildings near major transit stops and job centers. Despite high-profile opposition from some low-income tenants groups, the senators voting against the bill largely represent affluent suburbs.
To illustrate the geographical divide, a Twitter user put together this map of the senate districts and votes, with purple opposed, green in support (light for Democrat and dark for Republican), and blue abstaining:
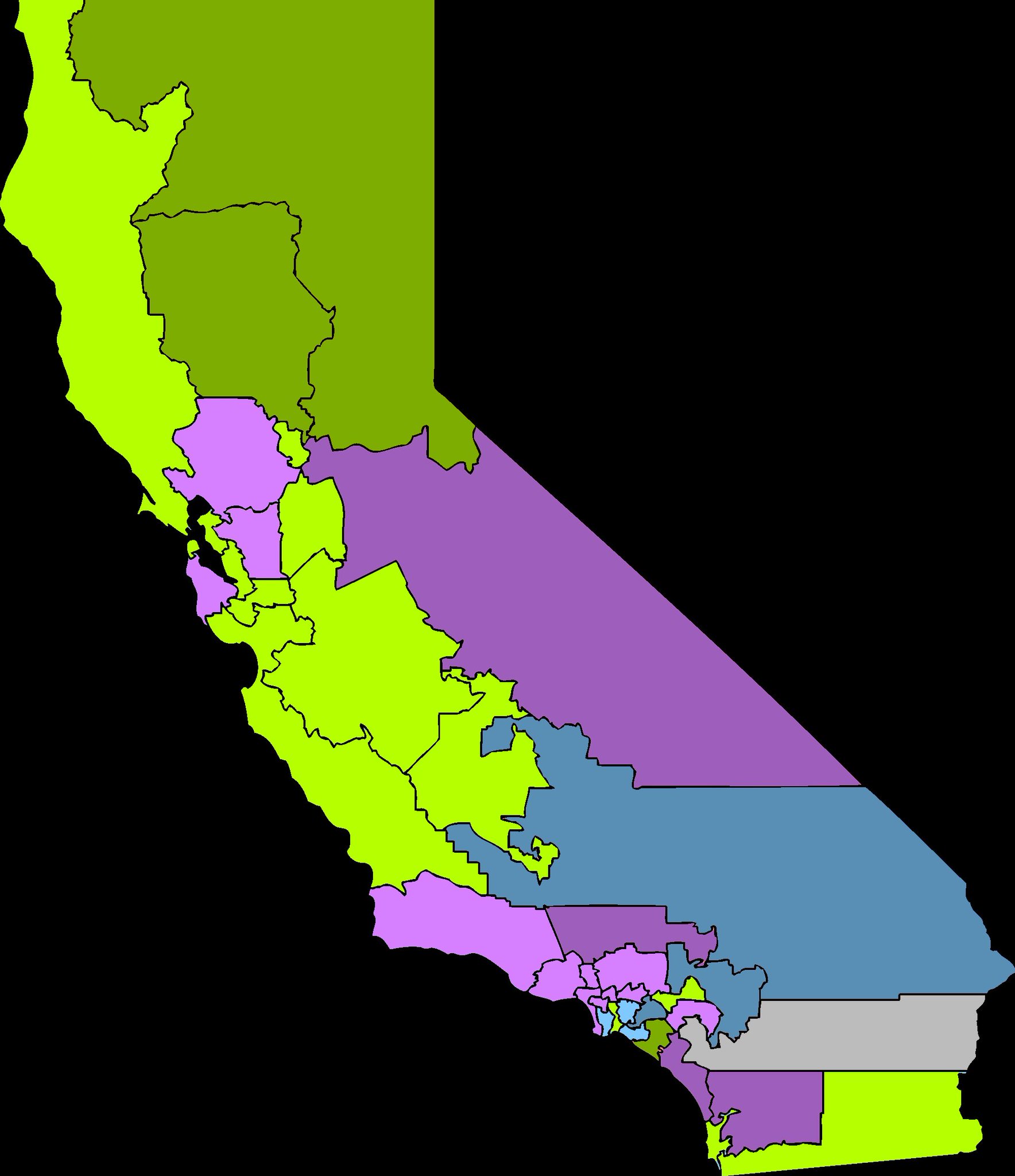
As you can see, the “opposed” senators largely cluster along on the affluent coastal and suburban areas. This dynamic is particularly apparent in the San Francisco Bay Area, where representatives of the urban core supported the bill (including bill author Sen. Scott Wiener and Sen. Nancy Skinner). But the senators representing the suburban, high-income Silicon Valley communities (Sen. Jerry Hill), affluent East Bay suburbs (Sen. Steve Glazer), and the Napa area (Sen. Bill Dodd) were all opposed.
Meanwhile, Southern California Democrats representing high-income coastal suburbs were almost uniformly opposed:
- Sen. Hannah-Beth Jackson, representing Santa Barbara communities;
- Sen. Henry Stern, representing Malibu and suburbs north of urban Los Angeles;
- Sen. Ben Allen, representing the Westside of Los Angeles, including Manhattan Beach and Beverly Hills;
- Sen. Anthony Portantino, representing La Cañada Flintridge and who had unilaterally shelved the bill last year in his committee; and
- Sen. Bob Hertzberg, representing the San Fernando Valley.
Notably, there were some standout “profiles in courage” votes in favor of the bill, including:
- Sen. Lena Gonzalez from Long Beach, despite opposition from city leaders in her district;
- Sen. Brian Dahle from the conservative, northern inland part of the state, who recognized the damage sprawl does to farmland;
- Sen. Bill Monning of Carmel who spoke passionately about the inequality and devastating commutes wrought by exclusive local land use policies; and
- Sen. John Moorlach of coastal Orange County, a Republican (and bill co-author) who appreciated the legislation giving more property rights to landowners.
What were the argument of opponents? They largely involved these issues:
“The bill will not produce enough affordable housing.” The bill in fact contained minimum requirements that projects receiving benefits under the bill include affordable units. As a result, SB 50-type reform would result in the biggest boost to subsidized affordable units in the state’s history, at possibly a seven-fold increase.
“SB 50 takes away local control.” To the contrary, the bill would give low-income communities five years to develop local plans for infill housing and two years for other communities to plan to meet these standards. Locals would be free to set more aggressive standards on affordability and relax restrictions even more if they wanted to do so. SB 50 also did not alter local permit approval processes. Furthermore, for senators who profess to care about the housing shortage, local control is the single biggest cause of the shortage, particularly through restrictive zoning.
“The bill will lead to gentrification and displacement.” This is a real, yet overstated, concern that the bill addressed with numerous provisions to protect against new developments displacing low-income tenants (a massive, ongoing problem that predates SB 50 and is made worse by the exclusionary housing policies SB 50 was designed to prevent). Furthermore, local governments were free to go beyond those protections. Second, as UC Berkeley’s Terner Center for Housing Innovation documented, any projects under the bill only “pencil” in high-income areas where developers get higher returns. Finally, as the Urban Displacement Project at UC Berkeley (in collaboration with researchers at UCLA and Portland State) found, new market-rate and affordable housing at a regional scale reduces gentrification and displacement overall.
Finally, Sen. Henry Stern uniquely argued against the bill for encouraging development in high-fire zones. It was an odd argument, considering that the SB 50 zones around transit are in some of the only non-fire, urban zones in the state, while the bill contained explicit language preventing application in high-severity zones. Furthermore, encouraging growth in infill areas reduces pressure to sprawl into the same wildlands Sen. Stern is worried about. Yet Sen. Stern was convinced that the protections weren’t strong enough and conceivably was worried that the provision in the bill allowing conversion of single-family homes into fourplexes would put more people into harms way. Given this logic, will Sen. Stern now support a bill banning new construction in high-fire zones? Or would he have supported the bill with an amendment banning such construction? He did not respond to these questions on his Facebook page.
So what’s next? The bill or some form of it could be brought back this legislative session as a “gut-and-amend” of an existing bill. Indeed, Senate pro tem Toni Atkins vowed shortly after the vote to bring a housing production bill back before the legislature this session. Supporters could also try a more limited approach, such as exempting controversial parts of the state from the bill.
Otherwise, given the long-term problem and entrenched opposition to change, the fact that such a landmark bill only fell three votes short is quite an accomplishment. Since the problem will only get worse, the political pressure to act will increase. That means that something like SB 50 will ultimately pass in California. It will be too late for those priced out in the near term, and possibly too late to address our 2030 climate goals, which will require reduced driving miles from housing closer to jobs and transit absent major technological innovation. But it will happen, because reforming our land use governance is the only way to solve this problem.

Bay Area legislators State Senator Scott Wiener (San Francisco) and Assemblywoman Buffy Wicks (Berkeley) will discuss housing legislation with me tonight on City Visions at 7pm, on 91.7 FM KALW in San Francisco.
Governor Newsom wants 3.5 million new homes built by 2025. How are our legislators planning to get us there? We’ll discuss Senator Wiener’s revamped Senate Bill 50, which encourages development around transit and job centers. And we’ll also find out Assemblywoman Wicks’ plans for this year, after she introduced a suite of housing legislation last year.
Tune in and ask your questions at 866-798-TALK! We’ll be streaming live at 7pm.

California State Senator Scott Wiener launched his third legislative attempt today at boosting California’s housing supply. SB 50 aims to address the state’s massive housing shortage, which has resulted in high home prices and rents, gentrification, displacement, inequality, homelessness, and a mass middle-class exodus to high-emission states like Texas and Arizona.
Because this housing undersupply is caused primarily by restrictive local land use policies in the state’s coastal job centers, Wiener’s approach has been to require cities and counties to allow apartment buildings near major transit centers. His first attempt in 2018 (SB 827) died quickly in committee. His second attempt last year (the birth of SB 50) was unilaterally shelved for a year by State Senator Anthony Portantino, who represents the affluent Southern California city La Cañada Flintridge (that city quickly became a poster child to housing advocates for high income single-family homeowners who don’t want to allow new residents in apartments into their neighborhoods).
The clock is now ticking on SB 50 in 2020. Under legislative rules, the bill must pass the full Senate by the end of this month — and first make it out of Sen. Portantino’s committee.
So Sen. Wiener is trying again, unveiling at an Oakland press conference this morning a critical amendment to delay statewide implementation for two years in order to give local governments the opportunity to develop their own plans that meet or exceed the housing, equity and environmental goals of SB 50. Otherwise, SB 50’s provisions relaxing height, parking and density requirements around major transit stations will automatically prevail.
Specifically, the state (through the Governor’s Office of Planning and Research) will develop guidance for these “local flexibility plans” by mid-2021. Cities and counties must then submit their plans for approval to the California’s Department of Housing and Community Development. That agency will then certify that the local plans are as stringent as SB 50. The local plans must be in place by January 1, 2023 in order to avoid defaulting to SB 50 statewide standards.
Otherwise, the substance of the bill remains essentially unchanged from last spring (here’s my rundown on the last changes before Sen. Portantino shelved it).
These new amendments seek to mollify critics who complained that the statewide approach undercuts local flexibility to meet the targets in a more tailored way. For example, rather than having uniform four-story apartment buildings around a major transit stop, perhaps a city would prefer to meet the overall housing production goals with a taller building in one spot and a shorter building across the street.
Will these changes be enough to satisfy local government objections? Probably not in many cases. The objections are less about local control and more about visceral dislike for apartment buildings and the residents they may bring. Arguments about local control — and relatedly against market-rate housing and instead building only subsidized affordable units — are often not made in good faith. Critics quickly move the goal posts as soon as amendments are made in their direction.
Take for example Sen. Portantino’s initial reaction to these amendments, complaining about not enough affordable housing, per his spokesperson to the San Francisco Chronicle:
“It was the senator’s hope that by taking a breath with SB50 it would focus efforts on actually building affordable housing as opposed to the market-rate housing predominant with SB50.”
This comment ignores that SB 50-type reform would result in the biggest boost to subsidized affordable units in the state’s history, at possibly a seven-fold increase. All without raising taxes or issuing bonds, and without delay about where to build these units even if public funds are available.
Still, these amendments may persuade critics who are on the fence. And perhaps most critically: will Governor Newsom now throw his weight behind the measure to help it pass? This is a big test for the governor on one of his signature campaign issues.
All in all, the next few weeks will be instructive as to whether or not California leadership can meaningfully address the the housing shortage and its severe equity, economic and environmental consequences.

California faces a dual crisis: a massive housing shortage leading to displacement and spiraling economic inequality; and an increase in driving miles and related greenhouse gas emissions which threaten to undermine the state’s progress achieving its climate goals. Both of these crises were solidly addressed in Sen. Scott Wiener’s SB 50, which seeks to ease local restrictions on housing development near transit and jobs, in part so more residents can access transit and shorter commutes.
The bill sailed through its first two policy committees, with bipartisan support and only one vote against it in each. Labor unions, business groups, and key environmental groups like NRDC supported it. Yet as my Legal Planet colleague Jonathan Zasloff posted yesterday, Sen. Anthony Portantino, chair of the appropriations committee, unilaterally suspended the bill until January next year.
Sen. Portantino’s political career started out in the affluent Los Angeles suburb of La Cañada Flintridge, a community of mostly upper income homeowners. Residents’ general state of housing security contrasts sharply with the rest of the region, with the city’s average household income in 2015 at $214,496, compared to a median income in Los Angeles County that year of $54,510. The city was also ranked the 71st wealthiest city in the U.S. by Bloomberg. In short, it is a community with residents who aren’t likely to feel the brunt of the housing affordability crisis and in fact are likely benefiting from it through increased property values.
Sen. Portantino’s arguments against the bill cited some familiar objections, such as the bill would increase gentrification (false: new construction under the bill would almost exclusively occur in high-income areas), it’s one-size-fits-all (false: it is tailored to counties by population and areas by transit frequency, with the exception of a statewide provision permitting fourplex renovations), and that it will discourage transit expansion if a new rail line would come with strings attached on land use (to which the obvious response is: why would we want to spend taxpayer dollars on expensive transit lines to low-density communities?).
He also argued that incentives would work better to convince local governments to allow more housing. Yet what incentives does Sen. Portantino and others who espouse this view believe will work to induce city councils in upscale communities like Palo Alto, Beverly Hills and La Cañada Flintridge to allow multifamily housing, particularly for a variety for income levels? These are wealthy communities that will not be moved by the prospect of more state dollars. Indeed, in recent years, some of them (like Corte Madera in Marin County) even tried to secede from regional transportation agencies to avoid having to comply with state mandates to build low-income housing — that’s right, they’d rather sacrifice state transportation dollars than live next to low-income people.
Sen. Portantino’s unilateral action to hold the bill until next year now places the burden on Senate president Toni Atkins to override this decision and allow SB 50 a vote by the full senate. It also places a burden on Governor Newsom, who has pledged to build 3.5 million housing units in the state and expressed tentative support for the concept of SB 50. Yet as UCLA’s Luskin Center documented, the state’s current zoning only allows for 2.8 million units, and most of those units are likely in places where we wouldn’t want to see new growth, such as in far-flung, fire-prone regions. In short, the Governor cannot achieve his signature campaign goal without significant statewide upzoning, as SB 50 would produce.
Will state leaders step up to resuscitate to the bill? Is it too late at this point? Or will those currently suffering from housing insecurity and lack of affordable places to live have to wait until next year for a solution, when an upcoming election may darken its prospects for passage? Certainly other bills in Sacramento seek to address aspects of the housing shortage, but only SB 50 presented a comprehensive, meaningful solution to a crisis that is well past time to solve in this state.
I’ll be discussing SB 50 (Wiener) on KQED Radio’s Forum this morning from 9am. The bill heads to its final committee hearing this Thursday before a full vote in the California State Senate.
As I’ve written before, SB 50 is the state’s first and only major attempt at comprehensive “upzoning” (relaxing local restrictions on housing) near transit and jobs. It also recently added a provision to legalize the conversion of single-family homes into duplexes, triplexes or fourplexes anywhere in the state.
Tune in at 88.5 FM in the San Francisco Bay Area and weigh in with your questions. Even if you don’t live in the Bay Area, you can stream it live and call in or email with questions.

Yesterday was a big day for SB 50 (Wiener), the bill to upzone residential areas near transit and jobs. The bill faced a potentially hostile Senate Governance and Finance Committee, chaired by State Senator Mike McGuire from Sonoma County and author of the rival Senate Bill 4. Despite the treacherous path, the outcome was a decisive win with only one vote against (Sen. Hertzberg of Los Angeles), albeit with significant amendments to the bill.
The new bill language has not been released, but based on the committee discussion and follow-up statements from Sen. Wiener and his office, the amendments essentially appear to do two big things (among other changes):
- Exempt SB 50 from counties with populations less than 600,000, except for cities within those counties with populations over 50,000 that have rail or ferry stops (see the green/purple parts of the flow chart below)
- Legalize “by right” permitting of single-family homes into duplexes, triplexes, and fourplexes across the state, albeit with only minimal demolition of existing structures allowed.
The amendments now make the overall bill relatively complex, but Berkeley-based artist Alfred Twu drew up this handy flow chart to explain how the bill will now work:

For a graphic on the counties now affected, here is a map from Barak Gila with the counties over 600,000 population (in which SB 50 applies) in yellow:
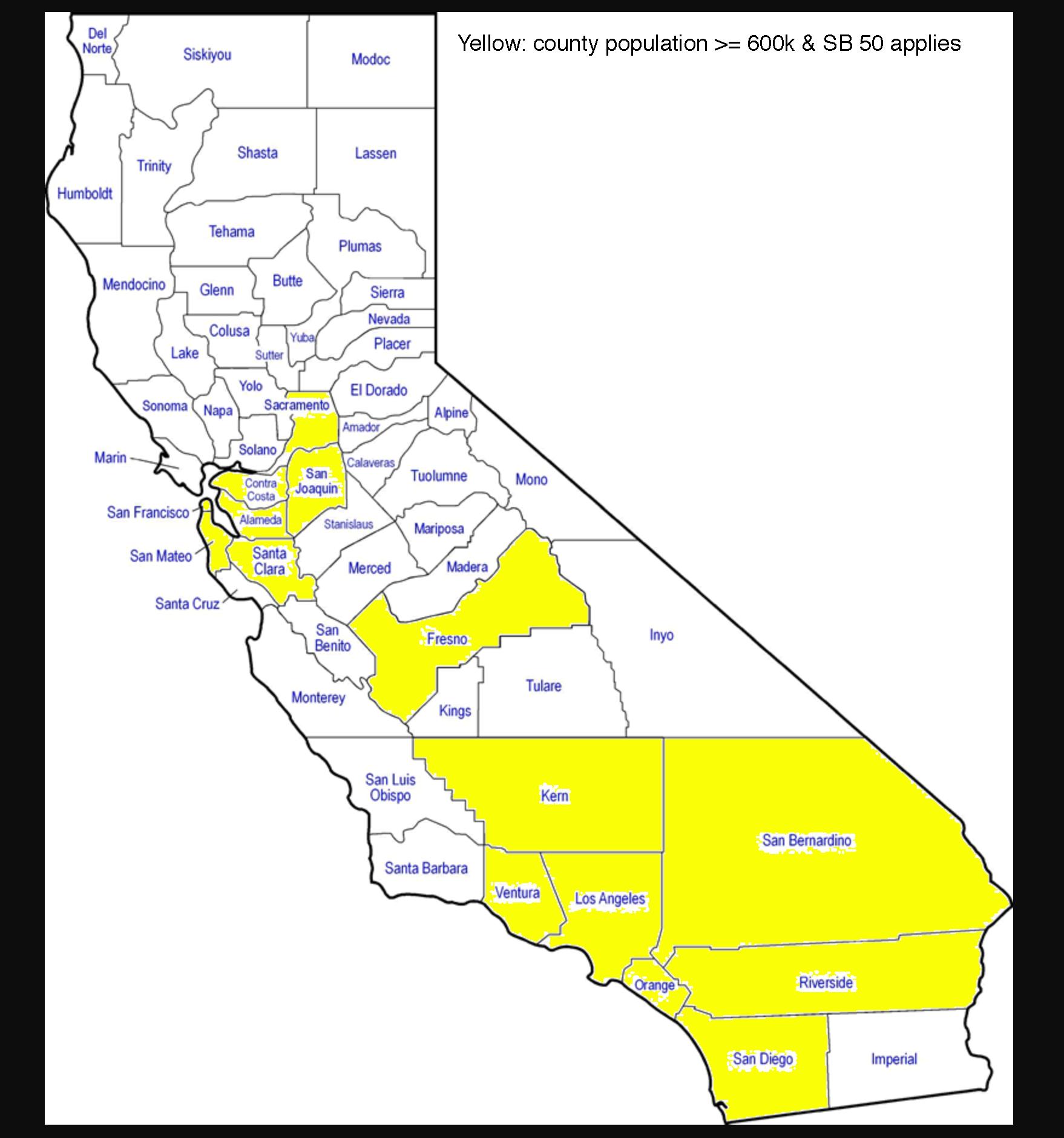
So did Marin County get a carve out, in a deal to merge the bill with county representative McGuire’s SB 4? Notable cities now apparently exempted from SB 50 include the SMART train and ferry stop in Larkspur and the ferry-stop towns of Sausalito and Tiburon. Yet San Rafael and Novato (two SMART train stops) are still covered by SB 50.
What about Sonoma County? Cities with SMART trains that no longer would be under SB 50 jurisdiction include Cotati, Rohnert Park, Cloverdale, Healdsburg, and Windsor. Still included are Petaluma and Santa Rosa.
In Southern California, Santa Barbara County’s Goleta and Carpinteria Amtrak stations also would not be covered by SB 50, while the City of Santa Barbara would still be affected.
Meanwhile, notable other cities with rail or ferry stops within those non-yellow counties, to which SB 50 will still apply, include Vallejo, Fairfield, Vacaville, Roseville, Rocklin, Madera, Modesto, Merced, Davis, Chico, Redding, and Salinas. And of course the remaining yellow counties represent major population and employment centers that could greatly increase housing production with SB 50 upzoning.
On balance, this new population criteria is not a bad compromise, as it means most of the core areas of California that prevent new housing are still affected. But the SMART train line is pretty well decimated by this compromise, as is the Santa Barbara Amtrak line. It’s a relatively small but painful price to pay, given the potential benefits statewide with the remaining areas.
Meanwhile, the fourplex by-right provision could potentially open up significant densification in California everywhere, a la the recent Minneapolis plan to end single-family zoning and allow triplexes city-wide. But could this new SB 50 provision encourage more high-density sprawl, with fourplexes in outlying areas that don’t have access to transit and therefore lead to more traffic and pollution? The original beauty of SB 50 (and its predecessor SB 827) was that it targeted transit neighborhoods to reduce overall driving miles. The fourplex provision could undermine those environmental benefits. Yet since the fourplexes (or other smaller divisions) can only involve minor demolition of existing structures (or building from the ground up on vacant parcels), the deployment may not be as sweeping as it might initially appear.
Overall, SB 50 cleared a major hurdle yesterday before its eventual advancement to the Senate floor, emerging relatively unscathed and with some potentially major new additions. If it passes that chamber, it will be on to the Assembly, with further carve-outs and compromises likely.

What’s the latest with California’s major proposed legislation to remove local restrictions on new housing near transit and jobs? I wrote back in December about Senate Bill 50 (Wiener), which would relax local requirements on density, parking, floor-area ratio and height (in some cases), for projects near transit and in high income “job-rich” communities that lack commensurate housing (read: Cupertino, home of Apple).
SB 50 also contains provisions to protect low-income renters from eviction from any new development under the bill and takes off the table (at least for the near future) large swaths of urban low-income areas deemed to be “sensitive communities.” For a visualization of what that means on the ground, see p. 11 (figure 5) of the CASA compact for a map of San Francisco Bay Area zones that would be exempted under this provision.
So how is the bill doing? Notably, SB 50 sailed through its first committee hearing last week with overwhelming approval. But it may face critical obstacles in its next hearing at the State Senate Governance and Finance Committee. That’s because that committee is chaired by State Senator Mike McGuire from Sonoma County, who authored a rival bill (Senate Bill 4) which would do much the same to relax local zoning near transit as SB 50, except with the big difference that it would exempt any “city with a population of 50,000 or greater that is located in a county with a population of less than 1,000,000” (which would exempt McGuire’s hometown of Healdsburg from the bill’s provision).
So the politics remain dicey going forward. The difference this year though is that Wiener has lined up powerful political support from organized labor, who like the job opportunities that would flow from more housing projects in urban areas. And by exempting in the near term “sensitive communities” with low-income tenants, Wiener has largely neutralized (for now) opposition from tenant groups who helped sink last year’s version, SB 827.
As a result, the opposition has so far been revealed as wealthy communities up and down California, who are resistant to allowing any new development or letting newcomers move in who can’t afford an expensive single-family home. They frequently use lines of attack like the bill is a “developer giveaway” or that proponents are “real estate shills.”
To counter these voices and win more support from advocates for low-income renters, Wiener has introduced amendments that tighten up the affordable housing requirements for any project that uses the bill’s provisions. Specifically, SB 50 now has ‘inclusionary zoning’ requirements in which developers with projects with between 20-200 units must make 15% of the units affordable to low-income residents (implemented on a sliding scale, with fewer units required if they’re available to extremely low-income residents), while 200-350-unit projects must provide 17% affordable units. Any project above 350 units must have 25% affordable units (also on a sliding scale depending on the income eligibility). Housing projects under 10 units are meanwhile exempt from providing any on-site affordable units, while projects of 10-20 units in size can pay in-lieu fees. With these provisions in place, the bill would likely lead to a significant deployment of subsidized affordable units to accompany new market-rate development.
But what practical effect will SB 50 likely have on the ground, assuming it can survive the messy politics and become law relatively intact? UC Berkeley’s Terner Center for Housing Innovation and Urban Displacement Project conducted an interesting case study policy brief and found that any likely boost to new housing under SB 50 would mostly be small scale and in high-income communities, though that impact varies depending on whether other local restrictions are in place.
The UC Berkeley study involved a parcel and financial feasibility analysis on four representative neighborhoods in the state, with the following highlights:
- Developers will get a much higher return on SB 50 projects in upscale areas, even with the higher land costs, meaning that most projects will be built in these areas and not in low-income areas (as I argued back during the SB 827 debates last year).
- Most of the available parcels (at least in these four study areas) are too small to support big projects, meaning most development will likely be of the 12-unit or less variety; in addition, the bill’s restrictions on developing properties with tenants will likely take a significant number of parcels off the table (a good thing, from the point of view of protecting current tenants from eviction).
- High on-site affordable housing requirements (discussed above) will be financially feasible in upscale areas but could sink projects in lower-income neighborhoods that otherwise barely pencil, so Sen. Wiener may want to consider a less rigid approach to the affordable housing requirements and instead scale them based on the value of the project.
- Remaining local government restrictions, such as high setback requirements and bans on projects that cast too much shadow (which was a dealbreaker for an important housing project in San Francisco that the board of supervisors just killed because it would cast occasional shadows at an adjacent park), will still impede projects, even if SB 50 passes.
- Developers may choose to ignore the benefits of SB 50 if a local government has already made it easy to permit projects at the current, locally determined height and density limits, just to avoid a protracted permitting fight that would come with using new, state-allowed higher limits.
The findings from this study should be clarifying for the SB 50 debate going forward. First, they show the relatively limited impact that SB 50 might have on the ground, at least compared to some of the hyperbolic rhetoric and initial studies about the predecessor bill’s impact in specific areas.
Second, SB 50 will likely end up being a just step (albeit a big one) in the right direction on boosting housing supply to match demand. Further reforms (some under consideration in other bills being debated this session) will need to focus on streamlining the permitting process for projects consistent with this new zoning. Otherwise, local governments are likely to respond to SB 50’s passage by adding more steps to the permitting process in order to kill projects through delay and multiple veto points. State legislation may also need to address the other zoning restrictions on new development that SB 50 leaves untouched, such as the aforementioned setback and shadow limits.
California’s current housing shortage certainly didn’t happen by accident — it’s the result of a complicated web of politics that SB 50 and its backers are trying to undo, piece by piece. We’ll have to stay tuned as more studies assess the bill’s impact and Wiener entertains more political compromises to win over support.
The California housing debate took me to KQED-TV’s “Newsroom” program on Friday. You can watch my discussion with host Thuy Vu and State Sen. Scott Wiener, author of SB 50 to upzone areas near major transit, at the 18-minute mark:
 Last year, State Senator Scott Wiener (D-San Francisco) went right to the heart of California’s massive housing shortage in its job-rich centers with SB 827, which would have limited local restrictions on housing near transit. The bill went down in committee, a victim of election year politics and diverse opposition from wealthy homeowners, tenants rights advocates, and even a few misguided environmental organizations.
Last year, State Senator Scott Wiener (D-San Francisco) went right to the heart of California’s massive housing shortage in its job-rich centers with SB 827, which would have limited local restrictions on housing near transit. The bill went down in committee, a victim of election year politics and diverse opposition from wealthy homeowners, tenants rights advocates, and even a few misguided environmental organizations.
Now Senator Wiener is back at it with Senate Bill 50, which retains most of the heart of SB 827 but with a few changes to address the anti-displacement concerns over low-income tenants who might be evicted with new infill development.
Here is a summary of the provisions:
- Easing local zoning restrictions on new housing: SB 50 would eliminate local restrictions on density and on-site parking requirements greater than 0.5 spaces per unit for residential projects within one-half mile of “major transit” (rail and ferry) stops, as well as projects within one-quarter mile of major bus stops. It would also reduce the minimum floor-area ratio (percentage of the parcel that is developed) and height restrictions to nothing less than 45 feet within one-half mile and 55 feet within one-quarter mile of rail and ferry stops. Notably, these height limits are lower than the original version of SB 827 but basically consistent with the amended version before it was killed in committee.
- Geographic applicability: SB 50 is both more and less restrictive in its applicable geography than SB 827. The one-half mile radius is consistent, but now it no longer applies to all half-mile areas around major bus stops. Instead, the bill only applies its basic provisions to one-quarter mile of high-quality bus stops (defined as having peak commute headways of 15 minutes or less). It’s more expansive though in that it now applies to communities that are determined to be “job rich” and affluent, but not necessarily close to transit. The Governor’s Office of Planning and Research and Department of Housing and Community Development (HCD) are charged with making the determination of what constitutes such a community, based on loose factors like proximity to jobs, high area median income relative to the relevant region, and high-quality public schools. And notably, the bill now applies to housing not just on residentially zoned land but land that may also be zoned commercial or mixed-use but allows for housing, too. But off the table (more below) are “sensitive communities” at risk of gentrification and displacement.
- Tenant protections & affordability requirements: the final amended version of SB 827 contained some strong anti-displacement provisions, and this bill picks up on those changes and expands them. For example, the bill does not apply to any properties that have tenants or have had a tenant within the last seven years. It also delays implementation in “sensitive communities” at risk of displacement until 2025, giving these areas from 2020 to 2025 to develop community-led plans to address growth and displacement. These communities would be determined by HCD based on factors like percentage of tenants below the poverty line, although it’s otherwise unclear how HCD would determine them. Finally, the bill includes minimum affordable housing requirement for projects requesting these local waivers (although that percentage is not yet determined yet in the bill).
With these changes, Sen. Wiener has already expanded the initial coalition in support — or at least not opposed at this point. For example, the powerful State Building & Construction Trades Council of California is supportive, as the bill explicitly allows existing local wage standards to remain unaffected. And tenants’ rights groups like Strategic Actions for a Just Economy in Los Angeles have not opposed the bill yet and have been in ongoing discussions with Sen. Wiener’s office. It otherwise seems inevitable though that the League of California Cities will oppose. So the question will be: will the coalition in support be powerful enough to override wealthy communities and their elected representatives, who will inevitably oppose?
In terms of the bill’s effectiveness, like SB 827 it would be a monumental shift in California housing policy that would address one of the core impediments to new housing construction: restrictive local zoning in job-rich areas.
Yet two provisions could undermine its effectiveness greatly, depending on how they are shaped during negotiations. First, the requirement to include a percentage of affordable homes in the buildings could render the provisions meaningless if that percentage is too high. For example, San Francisco’s voter-mandated inclusionary percentage of 25% affordable units for new development projects has contributed to a significant recent decrease in building permit applications (although other factors are at play as well), as SPUR recently documented.
In addition, placing off limits “sensitive communities” could also greatly limit its applicability without stricter and clearer criteria on how HCD will determine these communities and a sense of how many communities would be taken off the table. Otherwise the concept at first glance appears sound, as a way both to minimize opposition and reduce displacement risks in high-priority areas.
But overall, the bill retains the promise of SB 827 with a more inclusive process to bring on board more supporters. If SB 50 passes in something like its current form, it holds the potential to address the state’s housing shortage (and the emissions that result from long commutes from job-rich but housing-poor areas) in a fundamental way.


